 The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
ENCAPSULATION
Inspired by nature, novel PCM capsules show promise in study
Phase change material used in latent thermal energy storage systems must, of course, be encapsulated. The stiff containers, often made of high-density polyethylene, come in a variety of familiar shapes. The two most common are cylinders and spheres. Fins and dimples can be added to improve melting and solidification rates.
Researchers at Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China say they have identified a better shape. They found it in the circulatory systems of mammals.
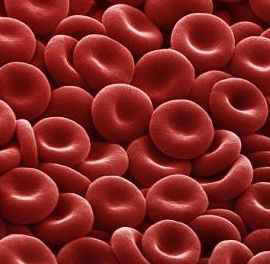 Red blood cells, or RBCs, are filled with hemoglobin, not PCMs, and their purpose is to deliver oxygen, not thermal energy. Still, the researchers wondered, is the distinctive biconcave shape conducive to more effective heat transfer?
Red blood cells, or RBCs, are filled with hemoglobin, not PCMs, and their purpose is to deliver oxygen, not thermal energy. Still, the researchers wondered, is the distinctive biconcave shape conducive to more effective heat transfer?
In a paper recently accepted for publication in Applied Thermal Engineering, “Thermal performance analysis of a novel PCM capsule in red blood cell shape,” Xiwen Cheng and Xiaoqiang Zhai described their investigation, in which they compared the RBCs with four other shapes by experimental and simulation methods.
All five tested shapes – RBCs, spheres, cylinders, drums and ring-shaped capsules – were sized to contain 25.5 grams of PCM (capric acid, lauric acid, palmitic acid). The sphere’s interior diameter was 40 mm. The shell material was nylon 12 with a thickness of 1.5 mm.
The researchers found that the RBC-shaped capsule performed significantly better than the other shapes. The average charging rate of the RBC capsule, for example, was twice as fast as that of the sphere.
Dr. William R. Sutterlin, Entropy Solutions’ chief science officer, who was not involved in this research, said he was intrigued by the results. “Until good alternatives are established to increase the thermal conductivity of the PCMs themselves,” he said, “novel designs such as these, which increase surface area, are welcome developments.”
PATENTS
Thermoregulating shawl and method of making same
U.S. patent application 20170086522 (Welspun India Ltd., Mumbai, India):
“A shawl article configured for thermoregulation, the shawl article comprising: an elongate panel having a first end, a second end spaced from the first end along a first direction, and opposed side edges spaced apart with respect to each other along a second direction that is perpendicular to the first direction, the elongate panel including a plurality of warp yarns that extend along the first direction. … The plurality of weft yarns include phase change yarns, wherein the phase change yarns comprise at least about 50% by weight of the shawl.”
Adhesive thermal gasket with PCM
 U.S. patent application 20170089648 (applicant Jones Tech, Cupertino, Calif.):
U.S. patent application 20170089648 (applicant Jones Tech, Cupertino, Calif.):
“An adhesive-thermal gasket, including: a body of thermally conductive material having a set of openings formed through the body; and an adhesive disposed into each opening for holding together a heat-generating component and a heat-dissipating structure as the body thermally couples the heat-generating component to the heat-dissipating structure. … The body [16] can be formed from a thermal pad, a thermal phase-change material, a graphite thermal interface material, etc.”
Flexible PCM sheet materials
U.S. patent application 20170087799 (applicant Smartpolymer GmbH, Rudolstadt, Germany):
“The invention relates to flexible PCM sheet materials having a high latent thermal energy storage density for the purpose of heat management. The flexible PCM sheet material includes a flexible supporting structure and phase-change-material elements arranged thereon separately in a specific geometry. The phase-change-material elements are geometrically defined structures composed of polymer-bound phase-change material. The flexible PCM sheet materials are characterized by a high latent heat storage capacity and optimized thermal conductivity, are dimensionally stable even in the event of temperature changes and after phase transitions, can be rolled, folded, wound, or cut to size without problems, and can be transported, stored processed, or used in a single layer or in multiple layers.”
BUILDING AND CONSTRUCTION
Forum on Germany’s VDI 2164 guidelines set for June 20 in Düsseldorf
Several members of the RAL Quality Association PCM will present lectures at the Expert Forum for VDI Guideline 2164, set for June 20 in Düsseldorf.
The Association of German Engineers’ building and building technology group (Verein Deutscher Ingenieure, or VDI) will host the meeting. VDI Guideline 2164 defines the fundamentals for latent-heat storage systems in buildings.
Dr. Bernd Boiting, chairman of the VDI 2164 committee, will present a brief overview of the guidelines. Other speakers include Esther Kieseritzky of Rubitherm; Marco Schmidt of BASF and Stefan Thomann, managing director of the quality association. The complete agenda will be available in a few weeks.IN BRIEF
• Ice Energy and Horizon Solar Power have completed the installation of a solar-plus-ice-battery-storage system at Palm Springs Cultural Center in California’s Coachella Valley. The system, which replaced an aging HVAC system, comprises 73.6 kW of solar panels and five Ice Bear 30s.
• The Trump administration’s budget blueprint is “just not correct” about the function of the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy, its former director said this week. The blueprint eliminates all ARPA-E funding “because the private sector is better positioned to finance disruptive energy research and development and to commercialize innovative technologies.” But agency was created just for stages of research and development that the private sector does not finance, said Ellen Williams, the agency’s director from 2014 until January 2017.
• Dow Chemical and DuPont won the blessing of the European Union for their $130 billion merger by agreeing to sell substantial assets, including key research and development activities.
• The global PCM market is expected to see a compound annual growth rate of 19.9 percent over the next five years, according to a new market research from Mordor Intelligence, “Global Phase Change Material Market-Segmented by Material Type, Product Type, Application, and Geography-Trends and Forecasts (2017-2022).”
• Kevin Bozec, marketing coordinator at Croda, will be among the presenters at the Plant Based Summit in Lille, France, April 25-27. He will discuss Crodatherm phase change materials in a session on new materials. To register for the conference and trade show, visit www.plantbasedsummit.com.
• GSA Business offers a closer look at the leadership transition at Alexium International Group Ltd., the company that took its flame-retardant material and PCM-based cooling fabrics to commercial markets in 2016.
• Two young German researchers, Modar Yasin and Felix Klinker of ZAE Bayern, were honored at World Energy Sustainable Energy Days in Austria earlier this month. They were recognized as best young researchers in the energy efficiency category for their paper, “Cooling performance of phase change material systems,” presented at the Young Researchers Conference.
RESEARCH ROUNDUP
For our full list of recent academic research, see puretemp.com/academic. Here are highlights from the past week:
From Energy and Buildings:• Synthesis, characterization and applications of microencapsulated phase change materials in thermal energy storage
From International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer:
• Fast charging of thermal energy storage systems enabled by phase change materials mixed with expanded graphite
• Experimental demonstration, modeling and analysis of a novel latent-heat thermal energy storage unit with a helical fin
From Journal of Applied Polymer Science:
• Novel phase change materials based on fatty acid eutectics and triallyl isocyanurate composites for thermal energy storage
From Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells:
• Preparation, characterization and thermal properties of fatty acid eutectics/bentonite/expanded graphite composites as novel form–stable thermal energy storage materials
From International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer:
• Parametric study and approximation of the exact analytical solution of the Stefan problem in a finite PCM layer in a steady periodic regime
From Thermal Science and Engineering Progress:
• Graphene nanoplatelets enhanced myo-inositol for solar thermal energy storage
From Thermochimica Acta:
• Novel model for the prediction of SSLE temperatures and crystallization paths of any mixture containing palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic and linolenic acid
From Construction and Building Materials:
• A comparative study on corrosion behavior of rebar in concrete with fatty acid additive as phase change material
From Building and Environment:
• Optimal cooling intervention for construction workers in a hot and humid environment
NETWORKING
Connect with PCM experts and industry leaders on LinkedIn
More than a thousand of your peers have joined a LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
You are invited to join the group and connect with PCM and TES experts from around the world. New members this week include Kevin Valentine, chief technical officer at CL India Pvt. Ltd., United Kingdom; Ashley Schultz, business development and sales account manager at Microtek Laboratories Inc., Dayton, Ohio; Jomi Thomas, head of foaming operations at Duroflex Ltd., India; and Tiago Silva, CFD and PCM researcher, Portugal.