 The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
IN BRIEF
• Researchers at the University of Alabama have won a three-year grant from the U.S. Department of Energy to develop a thermally activated building envelope system that integrates non-combustible phase change materials and hydronic activation into building envelopes. The goal is to reduce the energy costs as well as to support renewable energy sources for “power grid reliability, quality, resilience and dispatchability.” It’s one of 19 projects that will share up to $19.5 million in DOE grants for early-stage research and development for advanced building technologies and systems.
 • Viking Cold Solutions of Houston, Texas, has reached an agreement with Constellation to offer Viking’s commercial and industrial refrigeration customers access to the energy retailer’s Efficiency Made Easy program. The program helps businesses implement energy conservation measures with no upfront capital costs. The upgrades are included in the monthly charges that appear on a customer’s Constellation utility bill. Viking’s PCM-based thermal energy storage systems, such as the one shown at right, are designed to reduce energy costs by shifting peak demand to nighttime hours.
• Viking Cold Solutions of Houston, Texas, has reached an agreement with Constellation to offer Viking’s commercial and industrial refrigeration customers access to the energy retailer’s Efficiency Made Easy program. The program helps businesses implement energy conservation measures with no upfront capital costs. The upgrades are included in the monthly charges that appear on a customer’s Constellation utility bill. Viking’s PCM-based thermal energy storage systems, such as the one shown at right, are designed to reduce energy costs by shifting peak demand to nighttime hours.
• Registration is open for the 2019 Energy Storage Association Conference set for April 16-19 in Phoenix, Ariz. Exhibitors include battery thermal management startup Hotstart Inc. and Hydrostor, a Canadian company that offers “utility-scale energy storage facilities that can be flexibly sited using its Advanced Compressed Air Energy Storage (A-CAES) technology.”
• The deadline for submitting presentations for the Advancements in Thermal Management conference is Feb. 15. Topics include emerging technologies for thermal management; market opportunities for thermal products and services; thermal materials; and thermal modeling characterization and measurement. The conference will be held Aug. 7-8 in Denver, Colo.
• Sunamp Ltd. has appointed energy sector veteran Bill Edrich as global head of commercial and industrial to lead the thermal energy storage company’s growth plans.
 • Ice Energy says it has completed the first phase of what will be the largest installation of its Ice Bear thermal storage systems in the United States. Under a 21.6-megawatt energy storage contract with Southern California Edison, about 100 Ice Bear systems have been installed at businesses across SCE’s territory. The two-year project calls for the deployment of more than 1,200 Ice Bears.
• Ice Energy says it has completed the first phase of what will be the largest installation of its Ice Bear thermal storage systems in the United States. Under a 21.6-megawatt energy storage contract with Southern California Edison, about 100 Ice Bear systems have been installed at businesses across SCE’s territory. The two-year project calls for the deployment of more than 1,200 Ice Bears.
• Nominations are being sought for the World Materials Forum‘s 2019 Start Up Challenge. The competition honors “demonstrated breakthroughs” in a handful of categories, including new material composition and new product design. The top prize is 50,000 euros. The application deadline is Feb. 28.
• A group of businesses and environmental leaders have jointly launched the Plant Based Products Council, a group working to “guide the global economy toward more sustainable and responsible consumer products and packaging through greater use of plant-based materials.” The group’s website, pbpc.com, features a database of more than 480 plant-based and biobased products now on the market.
• Pelican BioThermal has opened a new network station and service center in Los Angeles to service, refurbish, repair and condition the company’s reusable Credo on Demand temperature-controlled shippers.
 • Tim Riazzi, right, president at Microtek Laboratories of Dayton, Ohio, has been elected vice president of the Phase Change Materials Industry Association of North America. He succeeds Pete Horwath, CEO at Insolcorp, who was elected president of the association in December.
• Tim Riazzi, right, president at Microtek Laboratories of Dayton, Ohio, has been elected vice president of the Phase Change Materials Industry Association of North America. He succeeds Pete Horwath, CEO at Insolcorp, who was elected president of the association in December.
• The CAVU Group of Dayton, Ohio, has posted an opening for a chemical engineer, “responsible for designing new process plants/equipment, work cells or modifying existing ones.”
• Registration is open for the 11th Microencapsulation Training School, to be held April 9-12 in Loughborough, United Kingdom. Topics include spray drying/cooling, dripping technology, membrane emulsification and microencapsulation in microfluidic systems. The training is hosted by Loughborough University‘s chemical engineering department. The deadline for early registration, with fees ranging from 450 to 1,000 euros, is Feb. 28.
• Registration is open for the 3rd Sustainable Oils & Fats International conference to be held April 4-5 in Paris.
• The presentations given Jan. 24 at the Workshop on Energy Efficient Buildings & Thermal Energy Storage Systems at the University of Nottingham are available for download. Among the highlights: “PCM Products R&D overview” (Adam Dicken), “Enhanced geothermal borehole heat exchangers with PCMs” (Heiko Gaich and Amandio Rebola) and “Phase change materials for renewable heating and cooling” (Sam Gledhill).
PATENTS
Mattress for improved sleep
U.S. patent application 20190038040 (applicant Technogel Italia S.r.l., Pozzoleone, Italy):
“Mattresses and mattress toppers having an upper layer including a high heat capacity material are disclosed. The mattress is configured to reduce a core body temperature of the body supported thereon, and thus induce improved sleep, measurable as an increase in the time spent in slow wave sleep relative to standard mattresses having lower heat capacities. The high heat capacity of the mattress may be attributable to the geometry and nature of the support material and optional additives, including polymer gels and phase change materials. Methods for improving sleep quality and uses of the high heat capacity mattresses to improve sleep quality are also disclosed.”
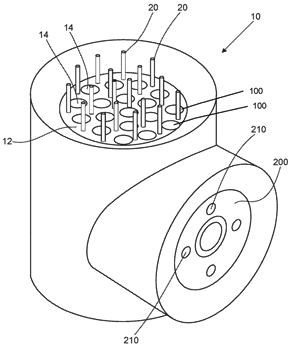 Thermal energy storage apparatus
Thermal energy storage apparatus
U.S. patent application 20190041139 (applicant Climate Change Technologies Pty. Ltd., Adelaide, Australia):
“A thermal energy storage apparatus, including: a block of a heat-absorbing material, and a plurality of heat storage elements, the heat storage elements including a phase change material stored in a containment vessel; wherein each heat storage element is in thermal contact with the block of heat-absorbing material. …
“The phase change material may include silicon metalloid or a eutectic, hypereutectic or hypoeutectic silicon composition.”
Aliphatic materials in heating and cooling applications
U.S. patent application 20190033009 (applicant Elevance Renewable Sciences Inc., Woodridge, Ill.):
“Aliphatic materials and their use in passive heating and cooling applications are generally disclosed. In some embodiments, dibasic acids and esters (diesters) thereof and their use in passive heating and cooling applications are disclosed. In some embodiments, C18 dibasic acids and esters thereof are disclosed, including their use in passive heating and cooling applications. In some embodiments, various olefins, including alkenes and olefinic acids and esters, are disclosed, including their use in passive heating and cooling applications.”
PCM evaporator and heat dissipating apparatus
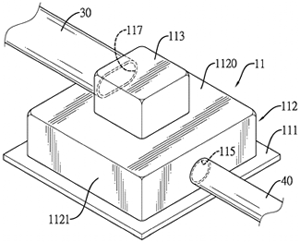 U.S. patent application 20190041144 (applicant Man Zai Industrial Co. Ltd., Tainan City, Taiwan):
U.S. patent application 20190041144 (applicant Man Zai Industrial Co. Ltd., Tainan City, Taiwan):
“A heat dissipating apparatus has a phase change material evaporator, a condenser, a refrigerant output tube, and a refrigerant input tube. The evaporator has a base having an evaporation chamber, a refrigerant inlet and a refrigerant outlet, a reinforcement panel mounted in the evaporation chamber and dividing the evaporation chamber into two spaces, and multiple heat conduction fins separately arranged in the two spaces. An opening area of the refrigerant outlet is larger than an opening area of the refrigerant inlet. The evaporator, the refrigerant output tube, the condenser and the refrigerant input tube form a closed refrigerant circulation loop with a refrigerant filled therein. Gas pressure of a gas-phased refrigerant in the two spaces can be increased. With pressure difference between the refrigerant outlet and the refrigerant inlet, the gas-phased refrigerant can be accelerated to flow toward the refrigerant outlet and flowability of the refrigerant can be increased.”
RESEARCH ROUNDUP
For our full list of recent academic research, see puretemp.com/academic. Here are highlights from the past week:
From Energy:• Effects of thermal conductivity and density on phase change materials-based thermal energy storage systems
From Renewable Energy:
• Melting process investigation of phase change materials in a shell and tube heat exchanger enhanced with heat pipe
From Applied Thermal Engineering:
• Compact latent heat storage decarbonisation potential for domestic hot water and space heating applications in the UK
• Numerical and experimental study of phase-change temperature controller containing graded cellular material fabricated by additive manufacturing
• A novel composite phase change material with paraffin wax in tailings porous ceramics
• Characterisation and evaluation of a new phase change enhanced working solution for liquid desiccant cooling systems
• Thermal properties enhancement and application of a novel sodium acetate trihydrate-formamide/expanded graphite shape-stabilized composite phase change material for electric radiant floor heating
From Environmental Research:
• Latent heat storage biocomposites of phase change material-biochar as feasible eco-friendly building materials
From Colloids and Surfaces A:
• A facile microencapsulation of phase change materials within silicone-based shells by using glass capillary devices
From Microporous and Mesoporous Materials:
• Phase change in modified metal organic frameworks MIL-101(Cr): Mechanism on highly improved energy storage performance
From Applied Energy:
• Role of porous metal foam on the heat transfer enhancement for a thermal energy storage tube
• Energy saving performance assessment and lessons learned from the operation of an active phase change materials system in a multi-storey building in Melbourne
From Building and Environment:
• Comparative analysis of the PCM application according to the building type as retrofit system
From Construction and Building Materials:
• Evaluation of the potential use of form-stable phase change materials to improve the freeze-thaw resistance of concrete
From Results in Physics:
• Application Research of Nano-storage Materials in Cold Chain Logistics of E-commerce Fresh Agricultural Products
From Journal of Energy Storage:
• Using PCM as energy storage material in water tanks: Theoretical and experimental investigation
NETWORKING
Connect with PCM experts and industry leaders on LinkedIn
 More than 1,400 people have joined a LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
More than 1,400 people have joined a LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
You are invited to join the group and connect with PCM and TES experts from around the world. This week we welcome Ralph Endemann, architect and founder of endeARKITEKTUR AS, Oslo, Norway; Ashley Sidi, digital marketing lead at Croda, New York, N.Y.; R. Chris Beck, maintenance coordinator at AECOM, Canada; Jan du Toit, managing director at Copil Technologies Pty Ltd., South Africa; and Matthew Aguayo, Ph.D., E.I.T., research scholar, Chandler, Ariz.