 The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
PHASE CHANGE MATERIALS
RAL Quality Association PCM works to spread word on phase change material
The RAL Quality Association PCM was established in 2004 to develop standards for the phase change material industry. Its European focus is reflected in its member list: BASF, Rubitherm, EMCO and va-Q-tec (Germany); Salca and global-E-systems (Netherlands); and Croda (United Kingdom). Sasol (South Africa) and Pluss Advanced Technologies (India) are also members.
 The annual membership fee is 4,000 euros plus a one-time admission fee of 2,000 euros. Members and non-members alike can submit their products to the association for independent testing and earn the RAL Quality Mark.
The annual membership fee is 4,000 euros plus a one-time admission fee of 2,000 euros. Members and non-members alike can submit their products to the association for independent testing and earn the RAL Quality Mark.
But the RAL Quality Association PCM does more than establish performance standards and conduct tests. We asked Stefan Thomann, the association’s managing director, to speak in detail about the organization’s objectives and the benefits of membership. He kindly responded by e-mail:
“Generally speaking,” he explained, “our association has two key objectives”:
1. Influencing the political landscape in the EU in favor of PCM
“The European Union has set ambitious targets in their 2020 Energy Strategy: reducing [greenhouse gas] emissions by 20%, increasing the share of renewable energy to 20% of consumption and achieve energy savings of 20% as minimum targets. The buildings sector is the one in which the largest savings in energy consumption and [greenhouse gas] emissions could be achieved. The Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD; http://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/topics/energy-efficiency/buildings) from 2010 was certainly a step into the right direction, requiring Member States to set minimum energy performance requirements for new buildings and buildings undergoing deep-renovation.
“One of our key points of criticism is that the EPBD and its national transpositions do pay a lot attention on insulation and efficient heating systems, but do not (sufficiently) address the problem of overheating and thermal comfort in summer. With the modern way of lightweight building these problems will undoubtedly increase or require cooling systems that will spend parts of the saved energy. Both you and I know that PCM would be a perfect solution via passive cooling systems or by combining HVAC systems with PCM. But unfortunately neither the EPBD nor 95% of its national transpositions allow to count PCM as an appropriate means of saving energy and getting incentives for them. We are intensively working on changing this at the moment, both on EU and national level.
“Another interesting aspect in terms of the Energy Strategy is promoting the use of thermal storages based on PCM. Since heat (or cold) is usually the form in which energy is needed, it makes sense to efficiently store thermal energy instead of inefficiently store electricity. This would help increasing the use of renewable energy by storing it from when it is available until when it is actually needed.”
2. Promoting the use of high-quality PCM
 “The other key objective is to provide high-quality PCM for the various applications, independently certified by the RAL Quality Mark. If customers decide to use PCM in their applications, they want to be 100% sure that the products perform in the way the supplier promised they would and continuously do over their anticipated lifetime. For this reason, we developed Quality and Testing specifications (RAL-GZ 896) for PCM and PCM composites, objects and systems.
“The other key objective is to provide high-quality PCM for the various applications, independently certified by the RAL Quality Mark. If customers decide to use PCM in their applications, they want to be 100% sure that the products perform in the way the supplier promised they would and continuously do over their anticipated lifetime. For this reason, we developed Quality and Testing specifications (RAL-GZ 896) for PCM and PCM composites, objects and systems.
“If manufacturers of PCM comply with the Quality and Testing specifications and can prove the continuous quality with an internal and external monitoring systems, they can use the RAL Quality Mark for their products as a well-acknowledged and independent proof of quality. …
“In my opinion, there is no better way to convince customers of the [value of] high-quality products compared to inferior but cheaper ones than having their long-lasting effectiveness independently confirmed and documented by the RAL Quality Mark. Although the RAL Quality Association is located in Germany, it is open for companies from all over the world and the Quality Mark can just as well be used in all countries – it is not limited to the German market.
“Apart from the actual use of the Quality Mark, I would say that the biggest benefit of being member is the close contact to some of the leading companies producing and applying high-quality PCM and products with PCM and to the European research facilities that are active in this area. [Members] have the right to attend all our General Assembly Meetings – which are about 3 per year at the moment – and to vote on all decisions … [and] shape the future of the Quality Mark and PCM in general.”
PATENTS
Garment steaming device with PCM
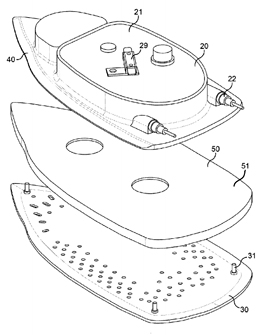 U.S. patent application 20150330014 (applicant Koninklijke Philips N.V., Netherlands:
U.S. patent application 20150330014 (applicant Koninklijke Philips N.V., Netherlands:
“The present application relates to a garment steaming device. The garment steaming device comprises a steam generator (20) having a heater (22) and an ironing surface (32) against which a fabric of a garment is locatable. An intermediate section (50) is disposed between the steam generator and the ironing surface to transfer heat from the steam generator to the ironing surface so that the ironing surface is indirectly heated by the steam generator via the intermediate section. The operating temperature of the ironing surface is not user selectable during use. … The intermediate section may comprise a body having at least one cavity containing a phase change material. The phase change material may be in one phase which will enable high thermal transmittance when the ironing surface temperature is low, for example, at 100° C. The phase change material will be in another phase which will enable low thermal transmittance when the ironing surface temperature is high, for example, at 145° C.”
Spray drying microcapsules with particulates
U.S. patent application 20150328615 (applicant Appvion Inc., Appleton, Wis.):
 “Spray drying microcapsules with particulates, the microcapsules that result from such spray drying, and compositions and methods of making said compositions including the spray-dried microcapsules. … Some or all of the microcapsules … can encapsulate a core material that includes one or more benefit agents. The benefit agent(s) can include one or more of chromogens, dyes, antibacterial agents, cooling sensates, warming sensates. perfumes, flavorants, sweeteners, oils, pigments, pharmaceuticals, moldicides, herbicides, fertilizers, phase change materials, adhesives, and any other kind of benefit agent known in the art, in any combination.”
“Spray drying microcapsules with particulates, the microcapsules that result from such spray drying, and compositions and methods of making said compositions including the spray-dried microcapsules. … Some or all of the microcapsules … can encapsulate a core material that includes one or more benefit agents. The benefit agent(s) can include one or more of chromogens, dyes, antibacterial agents, cooling sensates, warming sensates. perfumes, flavorants, sweeteners, oils, pigments, pharmaceuticals, moldicides, herbicides, fertilizers, phase change materials, adhesives, and any other kind of benefit agent known in the art, in any combination.”
CONFERENCES
Registration open for 2016 Energy Innovation Summit in Washington, D.C.
“Early bird” registration is open for the 2016 Energy Innovation Summit in Washington, D.C. The annual conference, hosted by ARPA-E and the U.S. Energy Department, brought together more than 2,000 entrepreneurs, researchers, industry leaders and government officials in 2015.
Advanced Cooling Technologies and the Electric Power Research Institute, which are developing PCM-based dry-cooling technologies for thermoelectric power plants, are among the 184 showcase participants now listed for this year’s summit.
Registration rates for the Feb. 29-March 1 conference will increase by $100 after Dec. 1. Graduate students seeking a complimentary pass must apply by Dec. 4.
IN BRIEF
• South African mines are using ice-based cooling systems to manage excessive heat. At depths approaching 3000 meters, temperatures can soar to 60° Celsius. Ice provides far more cooling energy than traditional water-based systems.
• Where to store all that intermittent wind-, water- and solar-generated energy? Stanford and University of California-Berkeley researchers suggest putting it underground.
• For the first time, emerging economies installed more renewable energy capacity than did wealthier nations last year, according to a new report by Bloomberg New Energy Finance.
• Zeolite-filled tanks designed to meet the solar-energy storage demands of a single-family household are yielding promising results in Austria. “We reached a storage density of 180 kWh/m³, which has never been achieved before in a device of this size,” said Wim van Helden, head of the research project at AEE INTEC.
• EnergyNest says it is encouraged by the initial results of its thermal energy storage pilot at Masdar Institute of Science and Technology‘s concentrated solar power installation in Abu Dhabi. The findings were presented at the CSP Today conference in Spain earlier this month.
RESEARCH ROUNDUP
For our full list of recent academic research, see puretemp.com/academic. Here are highlights from the past week:
From Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews:• Passive thermal control in residential buildings using phase change materials
From Energy and Buildings:
• Single layer mortars with microencapsulated PCM: Study of physical and thermal properties, and fire behaviour
• Experimental and Numerical Study on Thermal Energy Storage of Polyethylene Glycol/Expanded Graphite Composite Phase Change Material
From Energy:
• Experimental and numerical studies of hybrid PCM embedded in plastering mortar for enhanced thermal behaviour of buildings
From International Journal of Hydrogen Energy:
• Integration of phase change materials in compressed hydrogen gas systems: Modelling and parametric analysis
NETWORKING
Connect with PCM experts and industry leaders on LinkedIn
More than 440 of your peers have joined a new LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
You are invited to join the group and connect with PCM and TES experts from around the world. New members this week include Michael Cecchini of ECOterra Energy Consulting, Albuquerque, N.M.; Rob Falken, an inventor from Carlsbad, Calif.; and Reshma Ramakrishnan, a textile professional from Mumbai, India.
YOUR TURN
Got a question about PCMs or TES? Ask our experts
Two Entropy Solutions advisors, Dr. Mohammed Farid of the University of Auckland and Lucas B. Hyman of Goss Engineering, are ready to answer your questions about phase change material and thermal energy storage. We’ll select the best questions sent to inquiries@puretemp.com and post the answers here each Friday.