 The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
TRANSPORTATION

PCM heat-recycling system keeps tugboats ready for action
Tugboats are the tireless workhorses of the world’s rivers and harbors. These powerful watercraft must remain on standby for long periods, ready to assist other vessels at a moment’s notice. The energy required to keep the engines warm and the cabin comfortable in cold climates is usually derived from electrical shore power. That’s expensive and inefficient.
Kotug International BV has developed an on-board system that captures heat produced by the engines and stores it in a tank that contains phase change material. The Dutch company installed the heat recycling system on one of its tugboats, the ZP Bison, in 2016. The result: Shore power consumption has been cut in half on the Hamburg-based tugboat.
Koos Smoor, manager for fleet performance and innovation at Kotug, oversaw development of the system, which won the Maritime Innovation Award 2017 in November.
“The use of PCM technology is new in the maritime industry and has great potential not only for tugboats, but for every type of vessel, as it can be tailored to different spaces and user profiles,” Smoor said. “Kotug is looking into more applications for temperature control purposes.”
Smoor answered a few PCM-related questions by e-mail:
Q: When did Kotug begin developing the heat recycling system?
A: “Two years ago we tested heat storage on our hybrid tugs to reduce the ‘hotel load’ during standby. The hotel load is the generator load in kilowatts when the tug is not working. It is mainly heating or cooling and pre-heating of the main engines.”
Q: What type of PCM is used in the system (salt hydrate, paraffin, biobased)?
A: “We are still testing multiple PCM materials.”
Q: What is the PCM’s peak melting point?
A: “85 degrees is the ‘coolwater’ temperature of the engines. The coolwater of the main propulsion engines is used to heat up the PCM buffer. We also did test to use heat from the exhaust gasses to heat up the PCM buffer. However that is more complicated, and we stopped with that.”
Q: What is the PCM’s heat capacity?
A: “The heat capacity is 73 Kwhr/m3.”
 Q: How is the PCM tank configured, what are its dimensions, how much PCM is used?
Q: How is the PCM tank configured, what are its dimensions, how much PCM is used?
A: “The PCM tank [shown at right] is approximately 2 cubic meters. The PCM is warmed up by the coolwater of the engines. We like to keep the heat exchanger in the buffer for ourselves as we are working on a patent.”
Q: Who is the PCM manufacturer?
A: “The PCM material is manufactured in China.”
Q: How many tugboats are in Kotug’s fleet?
A: “Worldwide Kotug and its joint ventures consist of approximately 120 tugboats.”
Q: Are there plans to install the heat recycling system in other Kotug vessels?
A: “Yes, we are looking into more installations on more tugboats. The installation can be done during the five-year maintenance period cycle of the tugboat. Note: Many tugs operate in the tropics where there is no need to preheat the engines. On these tugs there is no application for PCM materials.”
Q: Are there plans to license the technology for use by other towage operators?
A: “We are still looking into this.”
PATENTS
Thermal energy storage apparatus
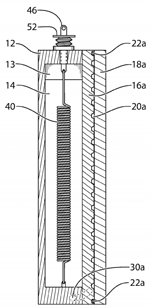 U.S. patent application 20180017337 (applicant NeoThermal Energy Storage Inc., Timberlea, Canada):
U.S. patent application 20180017337 (applicant NeoThermal Energy Storage Inc., Timberlea, Canada):
“A thermal energy storage apparatus is disclosed. The apparatus includes a base and fluid flow plates which cooperate with the base to define a cavity; a phase change material contained within the cavity; an extendable extension spring [40] at least partially contained within the phase change material [14]; and end plates which cooperate with the fluid flow plates to define fluid flow channels. Inlet and outlet ports allow for the ingress and egress of a heat exchange fluid into the fluid flow channels. In operation, the extension of the extendable extension spring induces solidification of at least a portion of the phase change material from a supercooled liquid state to a solid state, releasing thermal energy, allowing for the transfer of thermal energy across the fluid flow plates from the phase change material to the heat exchange fluid.”
Encapsulation of thermal storage medium
U.S. patent application 20180016482 (assignee University of South Florida, Tampa, Fla.):
“In one embodiment, a method for depositing metal on a polymer surface, the method includes coating the polymer surface with a binding metal to render the polymer surface solvophillic and/or hydrophilic and depositing a further metal on the binding metal-coated polymer surface.”
Anesthetic bandage with phase change material
U.S. patent application 20180015050 (inventor Ana R. Olivero, New Rochelle, N.Y.):
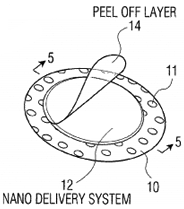 “A bandage for delivering an anesthetic through a patient’s skin at the site of a hypodermic injection prior to the administration of the hypodermic injection to alleviate pain due to the injection. The bandage has a first layer having a perimeter area adhesive, an anesthetic delivery layer disposed on the first layer inside the perimeter area and containing an anesthetic for delivery into the patient’s skin, a first peel-off layer covering the anesthetic delivery layer for keeping the anesthetic delivery layer sterile until the peel-off layer is removed, the first layer being placed on the skin of the patient at the future site of the injection with the anesthetic delivery layer and adhesive being in contact with the skin of the patient thereby to adhere the bandage to the site and allow the anesthetic delivery layer to deliver the anesthetic into the skin. … wherein the anesthetic delivery layer comprises a phase-change material that releases or stores energy to accelerate the delivery of the anesthetic into the patient’s skin.”
“A bandage for delivering an anesthetic through a patient’s skin at the site of a hypodermic injection prior to the administration of the hypodermic injection to alleviate pain due to the injection. The bandage has a first layer having a perimeter area adhesive, an anesthetic delivery layer disposed on the first layer inside the perimeter area and containing an anesthetic for delivery into the patient’s skin, a first peel-off layer covering the anesthetic delivery layer for keeping the anesthetic delivery layer sterile until the peel-off layer is removed, the first layer being placed on the skin of the patient at the future site of the injection with the anesthetic delivery layer and adhesive being in contact with the skin of the patient thereby to adhere the bandage to the site and allow the anesthetic delivery layer to deliver the anesthetic into the skin. … wherein the anesthetic delivery layer comprises a phase-change material that releases or stores energy to accelerate the delivery of the anesthetic into the patient’s skin.”
Cellulose capsules
U.S. patent application 20180019036 (applicant Technion Research & Development Foundation Ltd., Haifa, Israel):
“A method for making an oil-in-water dispersion or water-in-oil dispersion is disclosed. The method comprises the step of mixing a hydrophilic medium, a hydrophobic composition and non-derivatized cellulose solution in an ionic liquid. … The novel, highly stable nano/micro-scale slurries, based on cellulose encapsulated PCMs, have a relatively low viscosity at high concentrations, which increases their pumping efficiency and permits to increase the slurry concentration up to 45 wt. %, that allows to enlarge the efficiency of thermal energy transfer systems.”
Thermally insulated container assembly
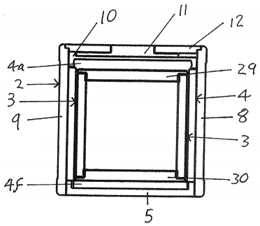 U.S. patent application 20180017311 (applicant Laminar Medica Ltd., Tring, United Kingdom):
U.S. patent application 20180017311 (applicant Laminar Medica Ltd., Tring, United Kingdom):
“The present invention provides a thermally insulated container comprising an expanded foam layer, a further layer, internal of the expanded foam layer, formed of a plurality of cool packs or insulation panels, and a locking lid. The cool packs consist of a combination of cool packs with stepped edges and individual side wall cool packs side wall cool packs formed with a living hinge, wherein the cool packs consist of a protruding fill point on one edge and blanking protrusions on the remaining three edges, and the cool packs comprise recesses on the top and bottom edges to accommodate either the fill point or the blanking protrusion of each adjacent cool pack.”
IN BRIEF
• PCM maker va-Q-tec AG officially opened its new North American headquarters in Langhorne, Penn., this week. Va-Q-tec will use the 20,000-square-foot facility to showcase new products and to manufacture its small temperature-control shipping containers. The location will also serve as a hub for the company’s rental and repair operation. “The investment in this new facility is a testament to our commitment to grow the business and expand our footprint in North America,” said CEO Dr. Joachim Kuhn.
• Drones that deliver sterile mosquitoes in the fight against the Zika virus will be field tested in Latin America early this year. The system, developed by the Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture‘s Insect Pest Control Laboratory, uses phase change material to keep the mosquitoes inactive during transportation.
• New from Greentech Media: “The Next Five Years in Energy Storage According to 500 Energy Professionals“
• New from Global Info Research: “North America Advanced Phase Change Materials (PCM) Market by Manufacturers, Countries, Type and Application, Forecast to 2022“
• New from Technavio: “Global Advanced Phase Change Materials Market 2017-2021”
• Viking Cold Solutions has begun installing its PCM-based thermal energy storage system in a 10,000-square-foot freezer at the Bashas food distribution center in the Phoenix area. The system, which consists of salt-hydrate-filled panels suspended from warehouse ceilings, is designed to significantly reduce energy costs by shifting peak demand to nighttime hours.
• The cost of renewable energy is falling so fast that it should be a consistently cheaper source of electricity than fossil fuels by 2020, according to a new report from the International Renewable Energy Agency.
• Utility Dive takes a close look at Nantucket Island’s “hybrid” plan to add energy storage, including thermal storage, to stave off expensive grid enhancements.
RESEARCH ROUNDUP
For our full list of recent academic research, see puretemp.com/academic. Here are highlights from the past week:
From Sustainable Cities and Society:• Simulation Research on the Dynamic Thermal Performance of a Novel Triple-glazed Window Filled with PCM
From International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology:
• Charging and Discharging Period Analysis of Myristic Acid as Phase Change Material [pdf]
From ASME 2017 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition:
• Design of a Latent Thermal Energy Storage System From Constructal Approach
From Advanced Engineering Materials:
• Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Systems with Solid–Liquid Phase Change Materials: A Review
From Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics:
• Solid-liquid phase equilibria of stearic acid and dicarboxylic acids binary mixtures as low temperature thermal energy storage materials
From Desalination:
• Comparative study on the solar still performance utilizing different PCM
From Science of Advanced Materials:
• Enhanced Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Performance of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)/Modified SiO2 Composite Phase Change Material
From Phase Transitions:
• Experimental research in the phase change materials based on paraffin and expanded perlite
From International Journal of Energy Research:
• Multiobjective optimization of a building envelope with the use of phase change materials (PCMs) in Mediterranean climates
From Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells:
• Preparation and thermal properties of exfoliated graphite/erythritol/mannitol eutectic composite as form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage
• Novel Na2SO4-NaCl-ceramic composites as high temperature phase change materials for solar thermal power plants (Part I)
From Energy and Buildings:
• Temperature stabilization using salt hydrate storage system to achieve thermal comfort in prefabricated wooden houses
NETWORKING
Connect with PCM experts and industry leaders on LinkedIn
 More than 1,100 people have joined a LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
More than 1,100 people have joined a LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
You are invited to join the group and connect with PCM and TES experts from around the world. New members include Marta Chafer Nicolas, green building innovation researcher at University of Lleida, Spain, and Alessandro Romagnoli, assistant professor in the School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.