 The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
The Phase Change Matters e-mail newsletter is a weekly summary of the latest news and research on phase change materials and thermal energy storage. To subscribe, visit www.puretemp.com/subscribe. For more frequent updates, follow @puretemp on Twitter or visit the Phase Change Matters blog, www.puretemp.com/pcmatters.
NEW PRODUCTS
Lexo tumbler uses material developed by University of Missouri professor
 The heat transfer experts at ThermAvant Technologies, founded in 2007 by two University of Missouri engineering professors, have developed a wide range of oscillating heat pipes, liquid cold plates and other thermal management solutions. Now the Columbia, Mo., company has introduced a stainless steel tumbler that uses biobased phase change material to keep hot beverages at the optimal temperature.
The heat transfer experts at ThermAvant Technologies, founded in 2007 by two University of Missouri engineering professors, have developed a wide range of oscillating heat pipes, liquid cold plates and other thermal management solutions. Now the Columbia, Mo., company has introduced a stainless steel tumbler that uses biobased phase change material to keep hot beverages at the optimal temperature.
The Lexo tumbler features three layers of 18/8 stainless steel and a BPA-free plastic lid. The 10-ounce version is selling for $37.95; a 16-ounce version will sell for $39.95. By comparison, Joeveo‘s 16-ounce Temperfect mug, available for preorder on Indiegogo, sells for $40. Ember Technologies‘ new Wi-Fi enabled temperature-adjustable mug, which employs PCM and a battery-powered heating system, sells for $149.95.
All three mugs use PCM to absorb the initial heat of coffee or tea and bring it to the optimal drinking temperature.
“Our mug takes about two minutes to cool to 140 degrees Fahrenheit, which is the optimal drinking temperature, and it stays there for up to eight hours,” said Dr. Bill Ma, the C.W. LaPierre Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering in the University of Missouri’s College of Engineering.
PATENTS
Systems and methods of using PCM in power plants
U.S. patent application 20170003079 (assignee Drexel University, Philadelphia):
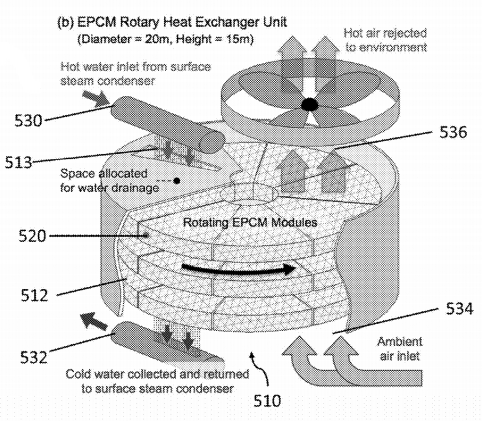
“Phase change material modules for use in a heat exchanger are described. The phase change material module comprises two or more set of a plurality of substantially aligned hollow structures arranged to form a porous structure. A phase change material capable of undergoing a phase change as a result of heat exchange between it and a fluid is housed within the hollow tubes. Also described is a phase change material module with hollow tubes having a cross-sectional area through the phase change material selected from elliptical, rectangular, stadium-shaped, teardrop-shaped, airfoil-shaped, rounded rectangle and ovoid. A heat exchanger comprising a plurality of the phase change material modules, a first fluid inlet and outlet, and a second fluid inlet and outlet, wherein the phase change material modules are repeated circulated from alignment with the first fluid inlet and the second fluid inlet is also described.”
Absorption body for a capsule containing a phase change material
U.S. patent application 20170003084 (applicant Cryogel, Paris):
“The invention relates to an oblong absorption body for a capsule for a refrigeration apparatus intended to contain a phase-change material, characterised in that said body comprises a flexible casing filled with gas at atmospheric pressure, having a main portion which is generally cylindrical, has a circular cross-section and ends in hemispherical end portions. The invention also relates to capsules provided with such an absorption body.”
Stadium ambient temperature control system
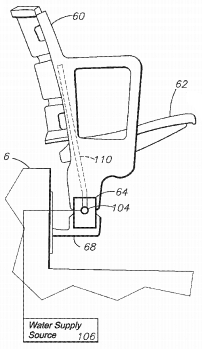 U.S. patent application 20170003042 (applicant Henderson Engineers Inc., Lenexa, Kansas):
U.S. patent application 20170003042 (applicant Henderson Engineers Inc., Lenexa, Kansas):
“A system for controlling ambient temperatures of exposed structures using phase change materials and/or tempered liquid delivery systems. Phase change materials may be fabricated to hold the surrounding temperature at a desired temperature, such as 70 degrees Fahrenheit / 21 degrees Celsius. As the heat load rises above this desired temperature, the heat is absorbed into the phase change material until that material has completely transitioned through its phase change, after which it will no longer absorb heat load. As the temperature then cools off at night, the heat is released from the phase change material, and the material changes back into its original phase. Phase change material may be placed within or on the exterior of stadium chairs. A liquid piping system may also be used to provide ambient heat control, including liquid piping for piping temperature-controlled liquid throughout the stadium while preventing condensation.”
PCM for cooling enclosed electronic components for solar energy collection
U.S. patent application 20170005615 (applicant GlassPoint Solar Inc., Fremont, Calif.):
“The present technology is directed generally to phase change materials for cooling enclosed electronic components, including for solar energy collection, and associated systems and methods. In particular embodiments, a system directs warm air through an airflow path in thermal communication with a phase change material to liquefy the phase change material and cool the air. The system also directs the cool air into thermal communication with electronic components to cool the electronic components via conduction and/or convection.”
IN BRIEF
 • Anthony Diamond and Amrit Robbins, cofounders of Axiom Exergy, have made Forbes’ annual list of “30 Under 30” in the energy category. The two developed a “refrigeration battery” that enables supermarkets and food warehouses to store thermal energy at night when power is cheaper. The battery, which uses salt-based phase change material, reduces peak power usage by up to 40 percent and provides backup cooling during power outages. The Berkeley, Calif., startup has raised $3.5 million from investors and, according to Forbes, has a $15 million sales pipeline.
• Anthony Diamond and Amrit Robbins, cofounders of Axiom Exergy, have made Forbes’ annual list of “30 Under 30” in the energy category. The two developed a “refrigeration battery” that enables supermarkets and food warehouses to store thermal energy at night when power is cheaper. The battery, which uses salt-based phase change material, reduces peak power usage by up to 40 percent and provides backup cooling during power outages. The Berkeley, Calif., startup has raised $3.5 million from investors and, according to Forbes, has a $15 million sales pipeline.
• Alexium International has reached a preliminary agreement to supply its Alexicool phase change material to New York-based Pegasus Home Fashions Inc. for use in pillows. Alexium, based in Perth, Australia, and Greer, S.C., says the deal is worth $10 million in annual sales of PCM.
• Eversource, New England’s largest energy provider, is seeking $21.5 million from the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities to fund energy storage demonstration projects for commercial and industrial customers. The utility plans to test ice storage and phase change materials. A related opening for an energy efficiency consultant is posted on the company’s website.
• The University of Birmingham has posted an opening for a research fellow in energy storage integration. The work will involve “optimising the operation of cryogenic and thermal energy storage in energy systems.”
• Engineering students at Southern Illinois University Edwardsville have developed a heat storage system that uses phase change material to store thermal energy from the sun during the day and release it after the sun sets.
• UCLA’s Energy Innovation Lab has an opening for a postdoctoral researcher in thermal energy storage. The lab is developing a high-temperature system that can provide high efficiency and performance at low cost using sulfur-based storage media.
RESEARCH ROUNDUP
For our full list of recent academic research, see puretemp.com/academic. Here are highlights from the past week:
From Journal of Energy Storage:• Empirical equations for viscosity and specific heat capacity determination of fatty acids
From Energies:
• Experimental Study on Specific Heat of Concrete at High Temperatures and Its Influence on Thermal Energy Storage
From Solar Energy:
• A novel medium-temperature form-stable phase change material based on dicarboxylic acid eutectic mixture/expanded graphite composites
From Energy:
• Techno-Economic Analysis of a Concentrating Solar Collector with Built-in Shell and Tube Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage
From Applied Energy:
• Effects of PCM on power consumption and temperature control performance of a thermal control system subject to periodic ambient conditions
• Cool colored coating and phase change materials as complementary cooling strategies for building cooling load reduction in tropics
From Construction and Building Materials:
• Porous inclusions as hosts for phase change materials in cementitious composites: Characterization, thermal performance, and analytical models
From New Journal of Chemistry:
• Porous organic–inorganic hybrid xerogels for stearic acid shape-stabilized phase change material
From Ecological Chemistry and Engineering A:
• Assessment of Passive Cooling in Residential Application under Moderate Climate Conditions
NETWORKING
Connect with PCM experts and industry leaders on LinkedIn
Nearly 1,000 of your peers have joined a LinkedIn group devoted to the discussion of phase change material and thermal energy storage. The Phase Change Matters group is an interactive complement to the award-winning blog and newsletter of the same name.
 You are invited to join the group and connect with PCM and TES experts from around the world. New members include Mark Richards, applications engineering manager at Phase Change Energy Solutions, Asheboro, N.C.; Dr. Pradyumna Goli, senior scientist at Henkel, Irvine, Calif.; and Glen Gabbard, co-owner, Gabbard Energy Group Inc., Sacramento, Calif.
You are invited to join the group and connect with PCM and TES experts from around the world. New members include Mark Richards, applications engineering manager at Phase Change Energy Solutions, Asheboro, N.C.; Dr. Pradyumna Goli, senior scientist at Henkel, Irvine, Calif.; and Glen Gabbard, co-owner, Gabbard Energy Group Inc., Sacramento, Calif.